Adding FTP, SFTP, and FTPS Servers
The FTP screen allows you to add and configure an FTP host to receive scheduled Argos reports that use the FTP task.
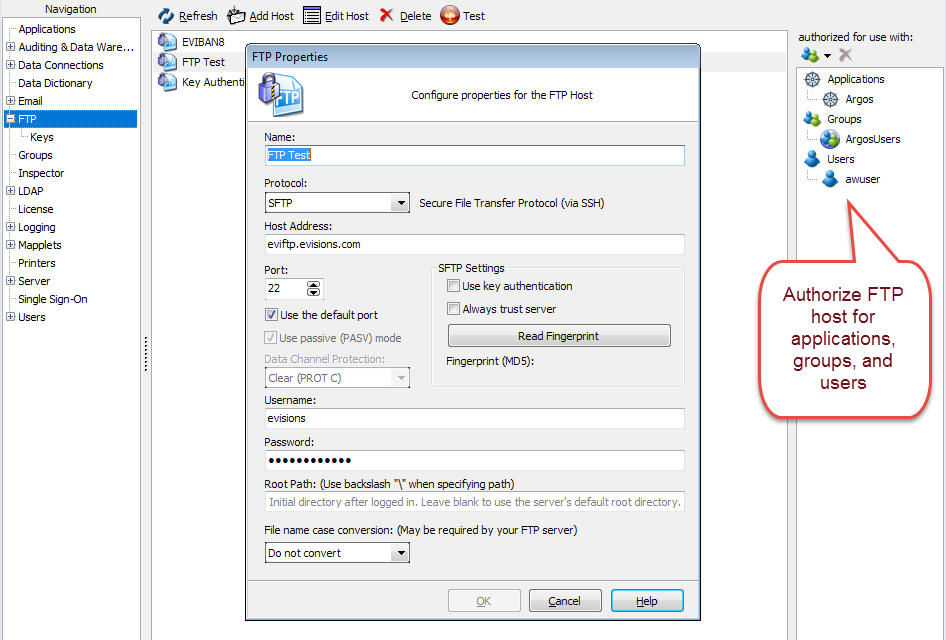
To add an FTP host click Add Host. Enter the following parameters in the FTP Properties dialog box:
- Name - The name of this FTP server as it will appear in the MAPS applications.
- Protocol - Choose the FTP, FTPS, or SFTP protocol, depending on your FTP server setup.
- Host Address - The IP address or hostname of the FTP server that will receive the reports.
- Port - The port on the server designated to receive files sent via FTP. If FTP or FTPS is chosen the default port is 21. For SFTP, the default port is 22.
- Use passive (PASV) mode - Passive mode for FTP/FTPS may be required if there is a firewall between users and your MAP server. It is enabled by default.
- Data Channel Protection - When using FTPS, you can specify that the data channel should be encrypted using "private" (PROT P) encryption instead of the default "clear" (PROT C).
- SFTP Settings - When using SFTP, you have the option to authenticate using a public/private SSH key pair instead of a password.
- Key - Select an authentication key for the designated SFTP server. Selecting Automatic from the list will enable MAPS to test each authentication key on the list, starting from the top, until a successful connection is made. If key authentication is not enabled, you will need to specify a password below instead. To add a private SSH key to MAPS, go to the Keys screen. The administrator of your SFTP server will need to add the corresponding public key to the SFTP server.
- Always trust server - If this option is checked, MAPS will not verify that the stored fingerprint matches the fingerprint from the server when using key authentication. You would usually only check this option when connecting to internal servers or testing environments where you are not concerned about man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Read Fingerprint - Request the public key fingerprint from the server. The fingerprint is a hash of the FTP server's public key, which MAPS stores in order to verify that it is connecting to the correct SFTP server.
- User Name- Obtained from the FTP server administrator.
- Password- Obtained from the FTP server administrator. Alternatively, for SFTP you may opt to use key authentication instead of a password.
- Root Path - By default, files sent via FTP are placed in the FTP root folder configured on your FTP server (or the home directory for the specified account, depending on the FTP server configuration). If you would like the files to be saved in a subdirectory, enter its local path relative to the FTP root.
- Use backslashes in the path regardless of the operating system on the FTP server. For example: \FTPtest\myfolder\
- All directories must already exist on the FTP server. MAPS cannot create new directories.
- Only subdirectories of the FTP root are valid paths.
- If you use a UNIX or Linux FTP server, keep in mind that paths are case sensitive and must match exactly.
- The user specified must have upload permissions to this directory.
- File name case conversion - Some FTP servers may require file names to be in all lowercase or all uppercase. Setting this option converts the file name entered by the user to the desired format.
You may choose any name you like for the FTP host. Your FTP server administrator will be able to provide the protocol, host address, port, username, password, root path, and any file name requirements.
Test FTP Host
To test the new FTP host, click the Test button to browse for a file. You will see a message indicating that the file was successfully transmitted, or alerting you of any errors.
Authorizing the FTP Host
Before you can send files to this FTP host, you must identify who is authorized to use it. In the authorized for use with pane on the right, select the applications, users, and groups that should be allowed to send files to this FTP host.